RBI Big Changes – भारतीय बैंकिंग सिस्टम को मज़बूत बनाने के लिए RBI के बड़े बदलाव
RBI Big Changes – The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced key reforms aimed at improving the strength, stability, and competitiveness of Indian banks. These changes align India’s banking practices with international standards.
भारतीय रिज़र्व बैंक (RBI) ने हाल ही में बैंकिंग सेक्टर में बड़े सुधारों की घोषणा की है। इनका उद्देश्य बैंकों को अधिक मज़बूत, स्थिर और वैश्विक स्तर पर प्रतिस्पर्धी बनाना है।
Key Highlights of RBI Policy
RBI की मौद्रिक नीति की मुख्य बातें
- Repo Rate unchanged: The repo rate remains 6.5%.
रेपो रेट 6.5% पर बरकरार। - GDP growth forecast: Increased from 6.5% to 6.8%.
GDP वृद्धि अनुमान 6.5% से बढ़कर 6.8% हुआ। - Inflation estimate: Decreased from 3.1% to 2.6%.
महंगाई दर अनुमान 3.1% से घटकर 2.6% हुआ। - Main Focus: Banking reforms for long-term stability.
मुख्य ध्यान: बैंकिंग सेक्टर को मज़बूत बनाने पर।
1. Risk-Based Deposit Insurance Premium
1. जोखिम-आधारित जमा बीमा प्रीमियम
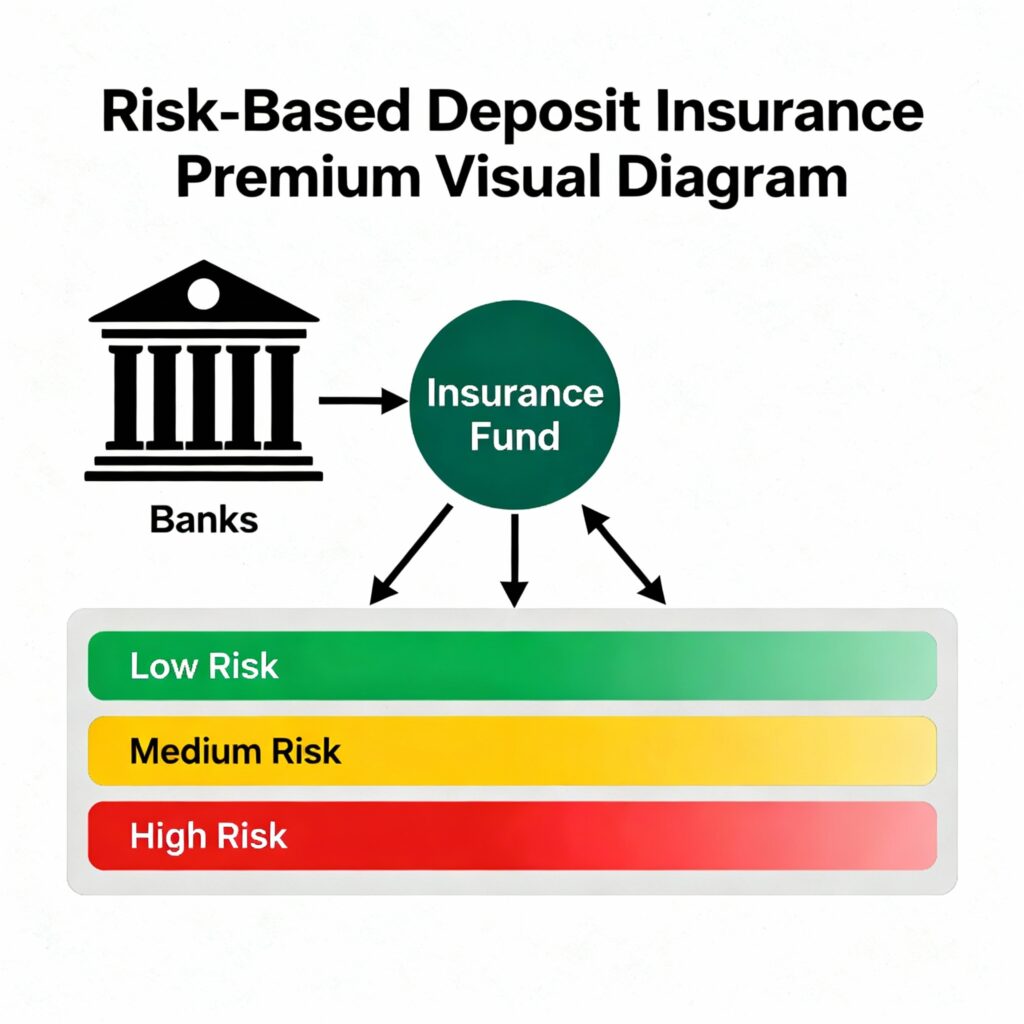
- Current System: All banks pay the same premium — 12 paise per ₹100 of deposits.
- Problem: Strong banks and weak banks pay equally.
- New System: Premium based on risk level.
- Strong banks pay less (e.g. 5–8 paise).
- Risky banks pay more (up to 12 paise).
Why Important:
- Promotes financial discipline.
- Encourages better risk management.
- Matches global practices.
Impact:
- Strong banks benefit with lower costs.
- Weaker banks push for improvement.
- No change for depositors — ₹5 lakh insurance remains.
हिंदी में सारांश:
अब बैंकों को उनकी जोखिम क्षमता के अनुसार प्रीमियम देना होगा। मज़बूत बैंक कम भुगतान करेंगे और कमजोर बैंक अधिक। इससे बैंकिंग सिस्टम अधिक निष्पक्ष और स्थिर बनेगा।
2. Expected Credit Loss (ECL) Framework
2. अपेक्षित क्रेडिट हानि ढांचा (ECL System)
- Old System: Provisioning only after loans turn bad (NPA).
- New System: Banks must predict future losses before NPAs occur.
- Start Date: April 1, 2027
Example:
If a bank expects ₹2 crore loss in future, it will set aside ₹2 crore now.
Benefits:
- Avoids sudden financial shocks.
- Improves long-term stability.
- Aligns with global standard IFRS 9.
हिंदी में सारांश:
अब बैंक भविष्य में होने वाली संभावित हानियों का अनुमान पहले से लगाकर तैयारी करेंगे। इससे बैंकों की बैलेंस शीट मज़बूत और सुरक्षित बनेगी।
3. Revised Basel III Capital Norms
3. संशोधित बेसल-III पूंजी मानदंड
- What It Means: Banks must keep enough capital before lending.
- New Rule Effective: April 1, 2027
- Change: Lower risk weight for
- MSME Loans
- Housing Loans
Why It Matters:
- Easier for MSMEs and homebuyers to get cheaper loans.
- Boosts growth in key economic sectors.
Impact:
- Encourages job creation through MSMEs.
- Makes housing loans affordable.
- RBI will monitor to prevent over-lending risks.
हिंदी में सारांश:
MSME और हाउसिंग सेक्टर के लिए ऋण देना अब आसान और सस्ता होगा। इससे रोजगार और आर्थिक विकास को बढ़ावा मिलेगा।
4. Relaxing Business Rules for Banks
4. बैंकों के लिए व्यवसायिक नियमों में ढील
- Current Rules: Banks and their subsidiaries (like insurance companies) must operate separately.
- New Rule: RBI will allow resource sharing — same offices, staff, or systems.
Why Important:
- Improves efficiency and reduces costs.
- Helps Indian banks compete globally.
- Encourages integrated financial services.
Impact:
- Cost savings for banks.
- Better services for customers.
- Higher profitability and stronger operations.
हिंदी में सारांश:
अब बैंक अपनी अन्य कंपनियों जैसे इंश्योरेंस या फाइनेंशियल सर्विसेज़ के साथ संसाधन साझा कर सकेंगे। इससे खर्च घटेगा और कामकाज तेज़ होगा।
RBI Big Changes – Conclusion
निष्कर्ष
RBI Big Changes – The RBI’s four reforms create a balanced approach — stronger risk management with more freedom for banks. Together, they will make India’s banking sector more secure, efficient, and growth-oriented — a key step toward the $5 trillion economy goal.
RBI के ये चार सुधार भारत के बैंकिंग सेक्टर को अधिक सुरक्षित और उन्नत बनाएंगे। इससे भारतीय अर्थव्यवस्था को 5 ट्रिलियन डॉलर के लक्ष्य की दिशा में गति मिलेगी।





















